The importance of aseptic technology to industries such as laboratories, medical facilities, and pharmaceuticals cannot be overstated. As science and technology evolve and medical standards increase, so does the need for a sterile environment. In this article, we will explore the importance of aseptic environments for laboratories and healthcare facilities and delve into what tools are used to maintain sterility in scientific research and medical practice.
To minimise the risk of contamination of people and the environment, Scitek offers a wide range of tools for use in sterile laboratories. These tools can be used for professional microbiological analyses or can be easily learned and used by beginners.
Cleaning/Disinfection/Sterilisation
Excellent cleanliness is the basis for ensuring aseptic operation. Tools are available to disinfect or sterilize the laboratory and the personnel before the experiment starts.
Surface disinfectant
Surface disinfectant is crucial for cleaning and disinfecting surfaces of laboratory bench tops, instruments and equipment. Its primary role is to prevent cross-contamination between samples or between laboratory equipment, a key aspect of maintaining a sterile laboratory environment.
Options: laboratory benchtops, glassware, workbenches, surfaces of experimental instruments, etc.
Hand and skin disinfection, skin cleansing and care
Hands and skin are the areas most likely to come into contact with bacteria and other microorganisms. Therefore, thorough disinfection of laboratory personnel is required to prevent potential bacterial contamination before performing aseptic experiments.
Options: Hand sanitizer, skin disinfectant, clean paper towels, etc.
Cleaning
Cleaning agents play a vital role in our laboratory. They are used to clean laboratory equipment and materials on a regular basis. Their main function is to remove dirt and attached microorganisms, thereby maintaining a hygienic and sterile laboratory environment.
Options: Cleaning cloths, cleaning brushes, washing liquids, etc.
Autoclave & Sterilizer
An autoclave sterilizer is a commonly used aseptic treatment equipment for inactivating bacteria, fungi, and viruses. It is used to effectively sterilize experimental equipment, culture media, culture apparatus, etc., to ensure the sterility of experimental samples and the experimental environment.
Optional: Petri dishes, culture flasks, experimental utensils, culture media, syringes, needles, test tubes, etc.
Benchtop Class N Autoclave
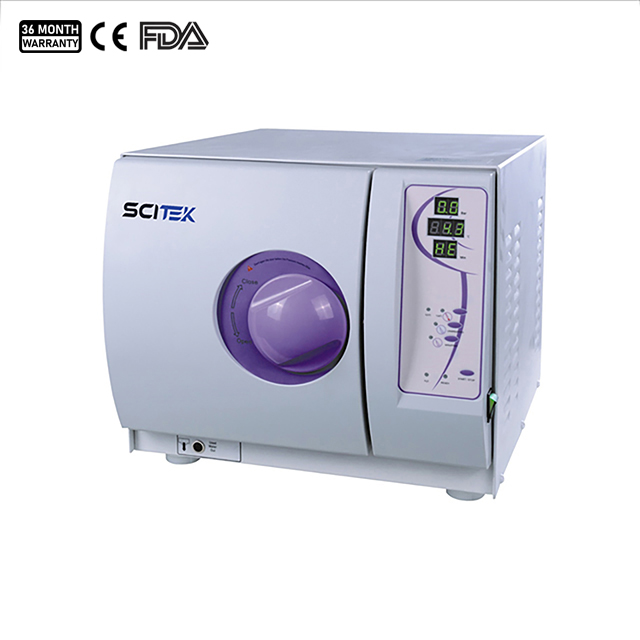 Benchtop Class N Autoclave
Benchtop Class N Autoclave
Display Accuracy : ±0.5℃
Recording Accuracy : ±0.5℃
Sensor Accuracy : 0.01℃
Capacity (L) : 16 / 18 / 24
Benchtop Class B Autoclave

Class B Autoclave
Design temperature : 139℃
Rated working pressure : 0.22Mpa
Rated working temperature : 134℃
Capacity (L) : 18 / 24 / 45
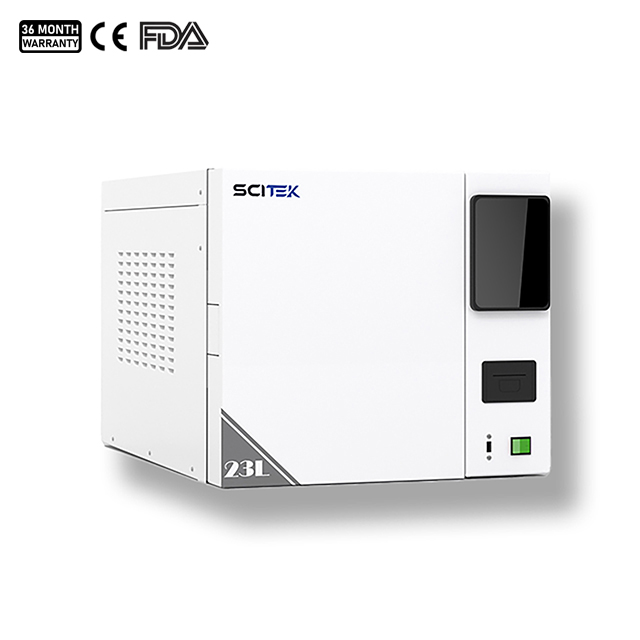

Benchtop Class B Autoclave
Display : 5.0 inch Color touch screen
Chamber Material : SUS304
Sterilization Temperature : 105~138 ℃
Capacity (L) : 24 / 29

Class B Autoclave
Rated Working Pressure : 0.22 Mpa
Temp Accuracy : ±1℃
Rated Working Temperature : 134℃
Capacity (L) : 24 / 29
Vacuum Autoclave

Horizontal Pulse Vacuum Autoclave
Design Temperaure : 150℃
Maximum Operating Temperature : 139℃
Maximum Operating Pressure : 0.25MPa
Volume(L) : 150 / 180 / 250 / 300 / 360 / 450 / 600 / 800

Vertical Pulse Vacuum Autoclave
Chamber Material : SUS304
Sterilization Temperature : 105~136 ℃
Designed Temperature : 150℃
Capacity (L) : 50 / 80 / 100 / 120 / 150
Experiment
Operator
Sterile Gloves are worn by the operator to prevent the contamination of samples or experimental equipment by hand bacteria.
Hand Sanitizer: Applied before the start of an experiment to ensure that the operator's hands are sterile.
Protective Clothing: Worn to protect the operator's body from contamination.
Laboratories
Surface disinfectant
It is used to clean and disinfect the surfaces of laboratory bench tops, instruments, and equipment to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
UV Disinfection System
UV Disinfectors use ultraviolet light's germicidal action to destroy microorganisms in the air and on surfaces. They are commonly used to disinfect worktops, instrument surfaces, and the air in laboratories.
Biological Safety Cabinet
A Biological Safety Cabinet is a key equipment used to manipulate biological samples under aseptic conditions. It provides a physical barrier during experiments and protects personnel and the environment from biological contamination through an air filtration system.
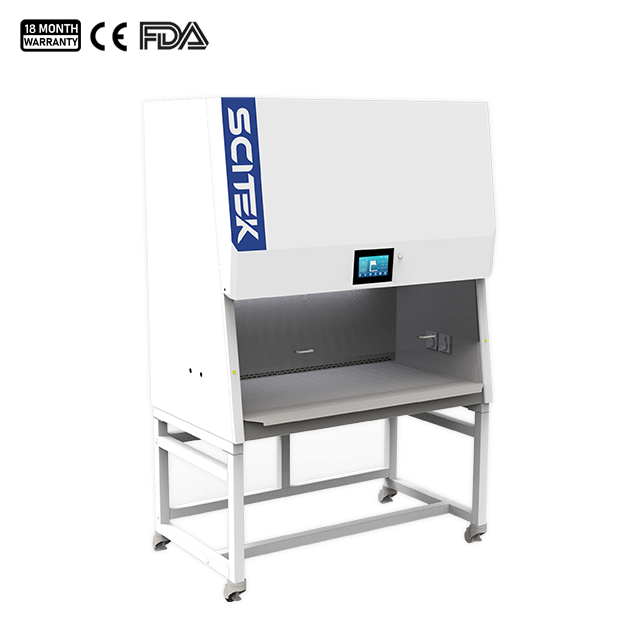

Biological Safety Cabinet Class I
Work Surface Height : 750mm
Airflow Velocity : 0.5~1 m/s, Speed adjustable
Sound Emission : ≤62dB(A)
HEPA Filter : 1 pcs, Efficiency: > 99.995% at particle size of 0.3 μm
Aseptic Technique Chamber
The aseptic technique chamber is a sealed environment that provides aseptic conditions and is typically used for manipulating cell culture and microbiological experiments.
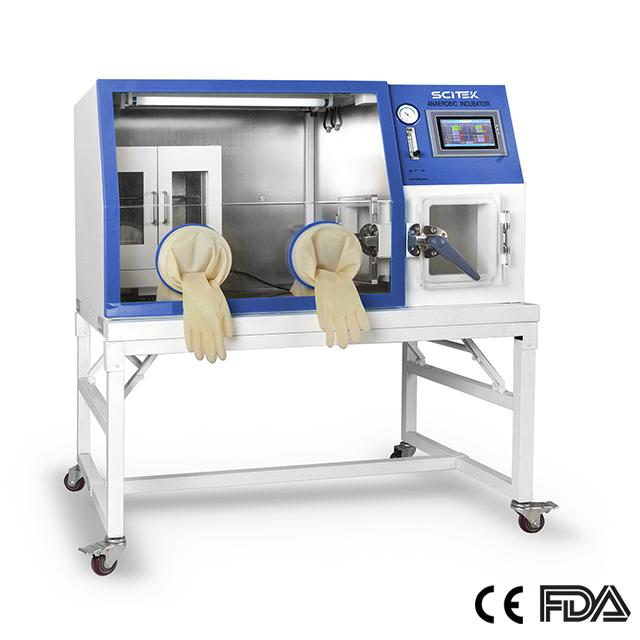

Anaerobic Chamber
Temperature Range : RT+3~60℃
Temperature Stability : <±0.3℃
Temperature Uniformity : <±1 ℃
Display Resolution : 0.1℃
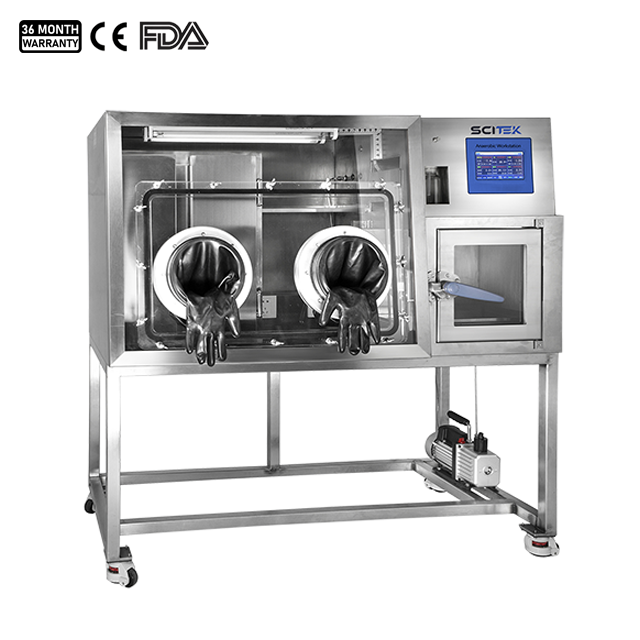

Anaerobic Chamber
Temperature Stability : <±0.3℃
Temperature Uniformity : <±1℃
CO2 Range : 0~20%
CO2 Control Accuracy : ±0.1%(imported sensor)
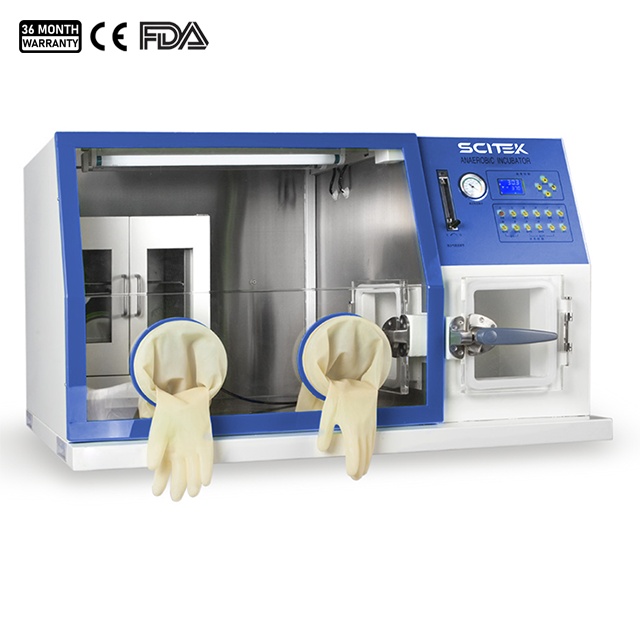

Anaerobic Chamber
Temperature Stability : <±0.3℃
Temperature Uniformity : <±1℃
Display Resolution : 0.1℃
External Size (W×D×H)(mm) : 1260x730x1380
Incubator
Incubators are used to culture bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms and provide constant temperature, humidity, and gas conditions to ensure the microorganisms grow in a sterile state.
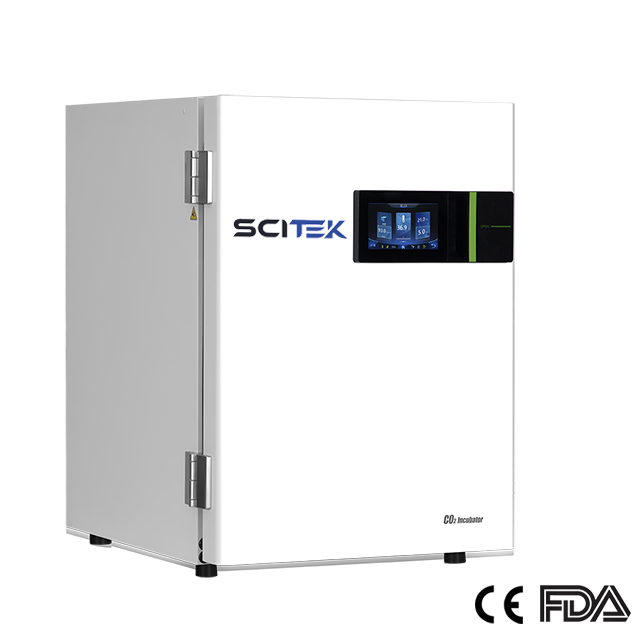

CO2 Incubator
Type Direct : Heat & Air Jacketed
Range : RT+3°C to 55°C
Uniformity : ≤±0.3°C
Accuracy : <±0.1°C
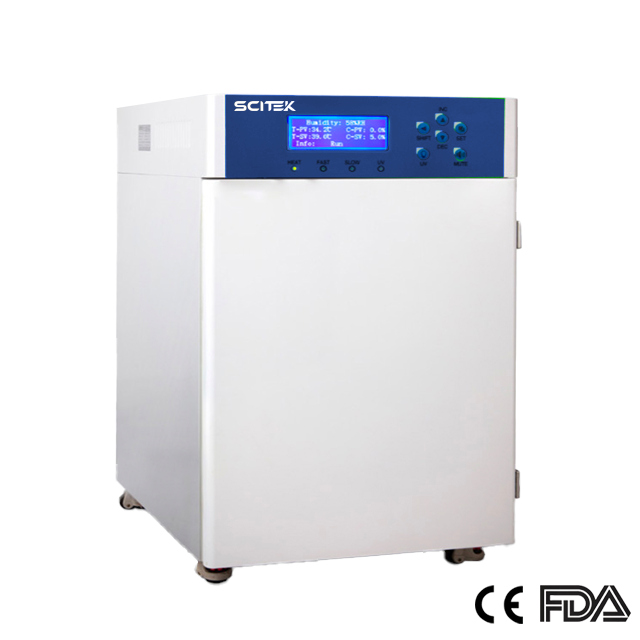

CO2 Incubator
CO2 Range : 0~20%
CO2 Control Accuracy : ± 0.1% (Imported sensor)
Humidity Method : Natural vaporization
Sterile Filters/Air Purifier
Sterile filters filter microorganisms from liquids or gases and are commonly used to prepare sterile media, solutions, and pharmaceuticals. They are used to maintain the sterility of the laboratory environment.
Laboratory Disinfectants and Cleaners
Choosing the right disinfectants and cleaners for regular cleaning and sterilization of laboratory equipment and instruments is important in maintaining a sterile environment.
Sampling/Shipping
Solid Samples
Sterile Forceps: used for manual sampling and transfer of solid samples, maintaining the sterility of the sample.
Sterile Scalpels: used when solid samples need to be separated or processed to ensure the sterility of the cutting operation.
Liquid Samples
Sterile Pipettes/Pipettors
Used to accurately aspirate and transfer liquid samples, ensuring aseptic sampling and pipetting.
Single-channel Electronic Pipette
Sterile Tips
Used with pipettes or pipette guns to ensure that the aspirated liquid is not contaminated.
Sterile Syringes
This is for accurate sampling and transfer of liquid samples, especially when volume adjustment is required.
Powder samples:
Sterile Weighing Paper (Sterile Weighing Paper): used to provide a sterile barrier between the weighing container and the sample when weighing powdered samples.
Sterile Weighing Spatula: This tool is used for sampling and weighing powdered samples, maintaining the sample's sterility.
Sterile Mortar and Pestle: used when grinding and mixing powdered samples to ensure sterility.
Importance of a sterile laboratory
Aseptic laboratories provide an environment that ensures that experimental samples are not contaminated by external microorganisms, thus guaranteeing the accuracy, reproducibility and scientific value of the results. Here is what makes a sterile laboratory important:
Ensure accuracy of results: Aseptic laboratories prevent contamination by external microorganisms and ensure the accuracy of results.
Preventing cross-contamination: Aseptic environments prevent cross-contamination between different samples, ensuring the independence and reproducibility of experiments.
Support for biotechnological research: The aseptic environment supports cell culture and biotechnological research, ensuring the success of experiments and the reliability of results.
Ensure medical safety: Aseptic laboratories protect the cleanliness of operating theatres, biomedical research and medical devices, ensuring medical safety and patient health.

 English
English



















